As an SEO beginner, it can feel like you have a tremendous amount to learn, especially when Google’s algorithm uses more than 200 ranking factors to rank content. Focusing on the basics of SEO, however, can help you build a strong foundation that will turn you into an SEO expert.
1. Claim (and complete) your Google My Business profile
Before you start researching keywords or writing title tags start with Google My Business.
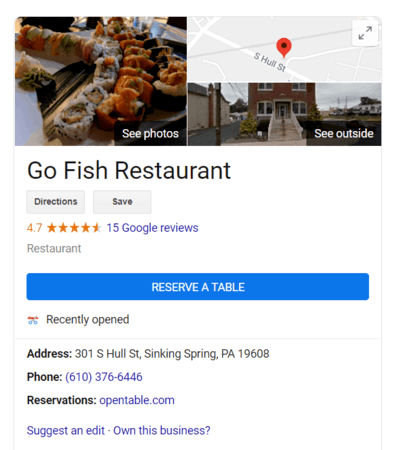
Google My Business is a free public profile or listing that appears in relevant search results on Google. You’ve probably seen Google My Business profiles when researching a brand, searching for a place to eat, or finding directions to a specific location.
Claiming (or creating) your Google My Business listing allows you to provide Google, as well as users, with immediate information about your company. It’s fast and easy to claim your account, too, so make this one of your first SEO to-dos.
Once you have ownership of your profile, optimize it by adding the following information:
- Name, address, and phone number (NAP)
- Operating hours
- Website URL
- Relevant categories, like “Restaurant”
- Brief description of what your company does and why it’s unique
- Photos
If you have any upcoming events, you can add them to your Google My Business profile too.
For the best results with Google My Business, stay active on it. Respond to user reviews, share posts about company happenings and offerings, enable text messaging, update company hours for holidays, and more.
2. Target long-tail keywords vs. short-tail keywords
Keywords are an essential part of search engine optimization.
If you want people to find your website (and if you want your content to rank in search results), you need to find relevant keywords, determine the search intent of users searching those keywords, and incorporate them into your meta tags and content.
Before researching keywords, it’s essential to review the difference between long-tail and short-tail:
- Long-tail keywords: A long-tail keyword is three to four words, like “how to roll sushi.”
- Short-tail keywords: A short-tail keyword is one to two words, like “sushi rolls.”
If you’re starting SEO for a website, you want to focus your keyword research on long-tail keywords. A long-tail keyword (because of its length) has less competition than a short-tail keyword, which makes ranking your content easier.
You can look at short- versus long-tail this way:
Short-tail keywords are like Olympic-level athletes, while long-tail keywords are like high school athletes. If you haven’t trained or built your site up to the Olympic level, you will struggle to rank at the top of search results. At the high school level, however, you have an excellent starting point.
3. Understand the 3 different search intents
In addition to long-tail and short-tail, you also need to consider the three user intents:
- Navigational: A person wants to go to a specific website, like Apple or Facebook.
- Informational: A person wants information about a topic, like how to roll sushi.
- Transactional: A person wants to buy a product, like a sushi roller.
It’s essential to understand these intents because they will influence which keywords you target.
A service or product page, for example, should target a transactional keyword while a blog post should target an informational keyword. If you search potential keywords on Google (before writing your content and optimizing your pages), you can determine the search intent by the results.
4. Research relevant keywords with the right tools
Once you know which keywords to focus on, you can start researching them with tools like:
| KEYWORD RESEARCH TOOL | PRICE |
|---|---|
| Google Autocomplete | Free |
| KeywordTool | $89-$199 / mo. |
| Google Keyword Planner | Free |
| KeywordsFX | Free |
| AnswerThePublic | $0-$99 / mo. |
You have a lot of free options as an SEO beginner, so experiment to see which one you like best.
As your SEO initiatives expand, you may think about investing in a paid tool, like KeywordTool. You may even decide to invest in an SEO toolkit, like Ahrefs, which offers tools for keyword research, competitor research, backlink analysis, and more.
5. Choose core (and related) keywords for every page
When you start optimizing your website, you’ll begin by researching core keywords for your pages.
For example, if you have an informational page about rolling sushi, you may make “how to roll sushi” your core keyword because of its high search volume. In addition to a core keyword, you also want to compile two to three related keywords.
You can find these keywords using your keyword research tools.
If you use Google as your keyword research tool, for example, you may look at the search engine’s “Searches related to [keyword]” feature, which appears at the bottom of search results, to find similar keywords. Or, you may use the autocomplete feature to discover other keywords.
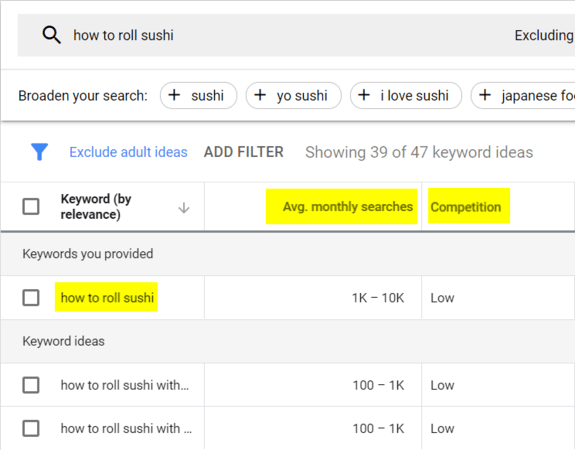
You can then enter those keywords into Google Keyword Planner to get the following data:
- Search volume
- Competition
- Bids
Once you have a list of relevant keywords, you can begin optimizing your content. For the best experience, create a Google Sheet and list your pages, as well as their core and related keywords. This sheet can then serve as a helpful reference for you and your team.
6. Optimize your title tags — and make them spicy
Your title tag is like that first meeting with someone new — it makes a first (and lasting) impression. That first impression also determines whether someone will click on your page or someone else’s, which is why informative, optimized, and spicy titles are a must.
What is an informative, optimized, and spicy title? Good question.
- Informative: Your title summarizes what your page is about, and without click-bait language.
- Optimized: Your title uses your core keyword and is 55 characters or less.
- Spicy: Your title gets readers excited and curious about your page and its content.
Keep in mind that your title tag appears in search results, not on your page.

If you want, you can create a different on-page title (via your H1 tag) for your content. For example, you may write the title tag, “How to Make Your Own Sushi Rolls (Infographic) | Allrecipes,” but then make the H1, “How to Make Sushi.”
Make sure, however, that your title tag and H1 coordinate with one another.
If users click on your site but then arrive on a page with a title that seems too distant from your title tag, they will bounce back to the search results. That action, from Google’s perspective, makes it seem like your content isn’t relevant to the user, which can lead to lower rankings.
Start writing your first set of title tags with help from the following tools:
Remember, you can always change your title tag later, so compile a list of titles to try.
7. Create informative and optimized meta descriptions
If you’ve browsed through some SEO beginner guides, then you’ve probably heard about meta descriptions, which appear below title tags in search results, and how they don’t serve as a ranking factor — unlike title tags.
That doesn’t mean you should exclude meta descriptions from your SEO strategy.

You want to include your keywords (and even related keywords) in your meta descriptions because of users. If someone searches for a keyword that appears in your meta description, Google will bold that keyword. For users, this can make your page seem more relevant, which can result in a click.

Now, it’s important to know that Google will often rewrite your meta description.

Even if you write a meta description that summarizes your content and matches meta description character limits (which are 150 characters), Google may still decide to re-write your content’s meta description.
That’s fine, it happens.
Still write a meta description, because if Google does use your meta description, it will feature your core and maybe even related keywords. Those keywords, if bolded, can help motivate users to click your site, which can send a positive signal to Google about your content and its relevance to the search.
8. Use keywords in headings and paragraphs
Another must-mention SEO tip for beginners? Insert keywords in your headings and content.
While Google would love not to rely on keywords, they’re a critical component to its ranking algorithm. Keywords help Google determine whether a piece of content is about a specific topic or query. That’s why your content (besides your title tags and meta descriptions) should use your keywords.

You want to include your core and related keywords in two places:
- Headings, like H1, H2s, H3s, and so on
- Paragraphs, lists, tables, and so on
For example, you should include your core keyword in your first paragraph if possible. If using your keyword at that point doesn’t seem natural, make sure to use your keyword within the first 100 words of your content.

Independent research from Clutch has named WebFX the top SEO company in the United States.
Over 150 WebFX clients have been interviewed by Clutch to discuss their experience partnering with us.Check out more Clutch reviews
Breaking your content into separate headings with H2 headings, for example, can help optimize your content and improve a visitor’s user experience. A heading makes your page easier for users to skim and read. It also helps users and web crawlers, which assist search engines in indexing your content.
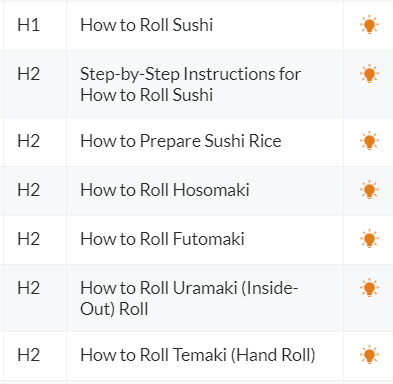
Depending on your related keywords, you can also use headings to target those keywords.
In the above example, for instance, the page targets the following core and related keywords:
- How to roll sushi
- How to roll hosomaki
- How to roll futomaki
- How to roll uramaki
- How to roll temaki
This approach allows the website to target its keywords, organize its content, and provide its readers with a skimmable experience. They can find what they need on the page fast, which makes them more likely to stay and less likely to bounce back to the search results — a positive signal to Google.
9. Write for humans first, then search engines
For many SEO beginners, it’s tempting to create and write content for search engines versus users. This approach can result in keyword-stuffed pages and title tags, as well as a tone of voice that seems robotic or unrelatable to users.
Put your audience first when creating and writing your content.
Think about what they’re looking to find, solve, or learn with your content. Then, consider how you could make learning, understanding, or resolving the problem even easier with your content structure, page design, or multimedia.
For example, this page about how to roll sushi uses images to help users learn.

From a user perspective, this approach makes sense.
What better way to learn about how to roll sushi than to follow along with a visual guide? If someone tried to explain how to roll sushi through text only, it would make the process confusing and make users unsure and nervous at every step.
Writing for your audience also matters because it’s through SEO that you hope to earn revenue. You want users to find you via search, but also convince them that you’re the perfect choice via your content. If you’re only writing for search engines, you cheat yourself of genuine leads and customers.
Put your audience first, and your optimizations second to get the most value from SEO.
10. Optimize content for featured snippets
Featured snippets appear in 50% of search results, so you want to optimize your content for them.
As a quick refresher, featured snippets appear at the top of select search results in what’s called Position Zero. This position places you above every other page, which can help your site earn more clicks and traffic.
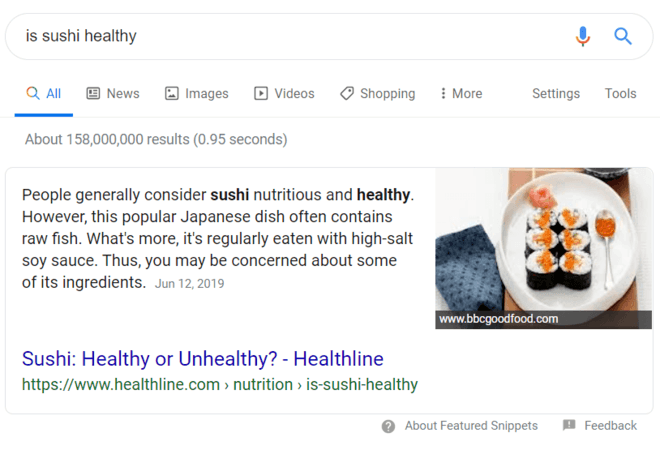
When you research your core and related keywords, you can check if the search results include a featured snippet. Make a note if they do. That way, you can remember to optimize your content for that featured snippet.
Start claiming featured snippets for your website with these SEO beginner tips:
- Answer featured snippets with tables, lists, or 46- to 84-word paragraphs
- Expand lists to eight-plus items (if useful to readers) to encourage clicks
- Create tables with three-plus rows (if useful to readers) to drive clicks
- Write dedicated headings for answering featured snippets, like “Is sushi healthy?”
- Use the core or related keyword that triggers the featured snippet as your heading
Keep in mind that your content will likely need to rank on page one to become the featured snippet. While the featured snippet sometimes goes to a site on the second page of search results, it’s extremely rare. Most featured snippets come from the top five pages.
11. Go ahead and link to other sites
Links are a critical part of SEO — in fact, they’re one of Google’s core ranking factors.
The emphasis on links, however, can make new SEOs hesitant about linking to outside content or sites. While you don’t want to link to a competitor site or link away from your site on a product or service page, you don’t want to avoid linking to external sites entirely.
For Google, internal and external linking is a sign of a healthy and genuine website.
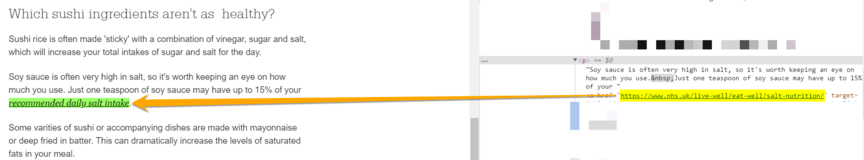
Feel comfortable linking to websites besides your own when writing informational content for your audience. Use links to back up and enhance your content, like by sharing a statistic, study, guide, or another supporting piece of content.
When linking to outside sites, remember to choose reputable, high-quality websites.
Sending your readers to a site that looks (or is) shady can hurt their opinion of your brand. It can also make Google wonder about the trustworthiness of your site. Keep your reader and your brand safe by only linking to websites that you would feel comfortable sending your grandma to visit.
12. Develop longer content
Repeated studies show that longer content, usually called long-form, performs better than short-form content when it comes to rankings, as well as social shares. That’s why your SEO strategy should consider (and probably include) long-form content.
For reference, long-form content is 1200 words or more, and short-form content is 500 to 800 words.
With long-form content, you can provide users with a complete guide to a topic.
If they’re researching the types of sushi, for example, they probably have follow-up questions that you can answer, like which sushi is the healthiest, where they can find the different types of sushi, and how much each type costs.
Keep in mind that while long-form content tends to outperform short-form content, that’s not always the case. In some instances, shorter content will rank at the top of search results. That’s why, before writing your content, you should always look at the search engine results pages (SERPs).
Remember, write for your audience first, and then for SEO.
13. Include keywords in URLs, but keep URLs short
URLs are another critical SEO tip for beginners.
For search engines and users, it’s helpful to have a short, descriptive, and organized URL. This kind of URL provides web crawlers with more context when it comes to your content and site architecture. It also helps users understand where they are on your website.
When creating URLs for your site, follow these tips:
- Include your core keyword
- Keep your URL to five words or less, if possible
- Use hyphens (-) to separate words
- Lowercase your URL
- Avoid apostrophes (‘) and hashtags (#)
Below, you can see examples of good and bad URLs:
| BAD URL | GOOD URL |
|---|---|
| example.com/blog/12345.html | example.com/blog/how-to-roll-sushi.html |
| example.com/sushi-rollers-2123123213.html | example.com/sushi-rollers.html |
| example.com/blog/Types-of-Sushi.html | example.com/blog/types-of-sushi.html |
Optimizing your URLs can make a big difference in your user experience and even rankings.
14. Establish a site structure now
When it comes to SEO basics, it’s essential to talk about site structure.
Your site structure, also called information architecture, refers to how you structure and organize your website. For example, what pages feature on your site’s navigation? How do you organize different site content, like blogs, products, or resources? And how does all your content relate to one another?
It’s a lot to think about, but it’s vital to SEO.
Start brainstorming how you’ll structure your site (or revise its structure) with these tips:
- Determine your website’s hierarchy: Your hierarchy refers to your site’s organization — think of it as a family tree. If your homepage is the parent, it’ll have several children, like /products/, /about/, or /blog/, and those children may have children, like /products/sushi-rollers/.
- Compile your header and footer pages: A website header and footer can help users, as well as search engines, navigate your site. You want to decide which pages or page links to include on those two elements. In most cases, these will be your most valuable pages or site sections.
- Design your pages with breadcrumb menus: A breadcrumb menu makes it easier for users to explore your site. Plus, a breadcrumb menu can serve as structured data, which can enhance your site’s look in search results. Work with your designers to include breadcrumb menus on pages.
While your site structure will require collaboration with your design and development team, it’s an essential part of SEO — even for beginners. That’s why you want to think about it now and incorporate it into your strategy.
15. Link your site to Google Search Console
Google Search Console is a must-have tool for any SEO’s toolkit.
This free platform (from Google), provides you with instant insight into your site’s performance in Google search results. It also helps you see how Google views your site. Plus, you can discover actionable ways to improve your website’s SEO.
For perspective, in Google Search Console, you can check for:
- Page impressions and clicks from different queries
- Crawl errors
- Mobile-friendly issues
- Rich results markup
- Page indexing
- Page rankings
- Page speed ratings
- And more
You can also submit your URLs (or entire site) in Google Search Console.
With all the features and insights that Google Search Console offers, every SEO should use it. Set up Google Search Console for your website by following the “Get started with Search Console” guide from Google.


Pingback: Three Ways Any Business Can Drive Traffic to their Online Store - InterWeb SA
Pingback: 15 SEO Tools to Optimize Your Website for Success in 2021 - InterWeb SA